[注:本站登载的某些文章并不代表本站支持或反对其观点或肯定其真实性]
| The building of the future will not just sit on a lot – it will breath, sleep, and wake up in the morning. And it will be beautiful。

When Fortune invited my design firm, which specializes in sustainable architecture, to share our vision of a building of the future, we decided not to guess about conditions decades or centuries away. Instead, we looked at the possibilities that exist now.
Buildings consume 40 percent of our energy and can have life spans longer than humans. Because we live, work and associate with others in buildings, they form part of the fabric of human life—and thus have an enormous effect not only on the quality of individual lives but also on the state of the earth.
In the pages that follow, we have configured a structure that is not just kind to nature; it actually imitates nature. Imagine a building that makes oxygen, distills water, produces energy, changes with the seasons—and is beautiful. In effect, that building is like a tree, standing in a city that is like a forest. -- By William McDonough, founder and principal of William McDonough & Partners。

Form and function
Curved forms increase structural stability and maximize enclosed space; this reduces the amount of materials needed for construction. The shape is also aerodynamic, diffusing the impact of wind.

Treetops
Traditional rooftops, covered in asphalt and tar, create heat-absorbing surfaces that contribute to the "urban heat island" effect—higher temperatures that can alter weather patterns and intensify smog. A layer of ground cover on this building's roof helps to regulate temperature, protects waterproof coatings, and absorbs and cleans storm water.

Soil and green
The western side of the building is a series of three-story atrium gardens. The greenery brings the outdoors inside, providing a breath of nature. Plants clean the interior air, and as leaf colors change, the building reacts in step with natural cycles. The north façade (unseen) is clear glass covered with positively-charged mosses that absorb particulates of the air.

Water, water
Water is recycled in the building several times over. Greenhouses treat wastewater from sinks and bathtubs for reuse as irrigation in the building's gardens, a process made possible when nontoxic cleaning products are used. Cleansed by the gardens, the water can be used again as non-drinking water—for example, in toilets. 
Street smarts
After a close study of the sun and shadows, the shape and orientation of the building are tailored to the site. This building faces south toward a park, so it can capture maximum sunlight, and its irregular form allows more daylight to reach the street. Gardens circle the base, contributing to the quality of life at street level. 
Solar power
The southern façade, made of about 100,000 square feet of photovoltaic panels that convert sunlight into electricity, collects enough energy to provide up to 40 percent of the building's needs. Costing at least 20 cents per kilowatt-hour—several times as much as coal or natural gas—solar PV is expensive today. But the trends are good: Solar is getting cheaper, and the relative economics will improve as more states and countries regulate the production of greenhouse gases.
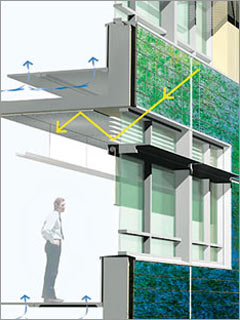
Building skin
The structure is built up in layers of materials that perform different functions, from weatherproofing to insulation to transparency. These surfaces are becoming thinner, lighter, and smarter.

Productive workspaces
Under-floor air distribution improves air quality. Flexible communal spaces replace fixed individual stations. Chairs and workstations are ergonomic. Smart monitors detect the presence of people and adjust temperature, light, air, and sound as needed. This allows individuals to control their environment. Our motto: "We don't heat or cool ghosts." 
Waste equals food
In nature, nutrients are cycled and recycled endlessly. "Eco-effective design" seeks to mimic those cycles. All products, from building materials to furnishings, are designed to return safely to the earth or to be reused—like office chairs that can be disassembled into components and sent back to the manufacturer to become another product. 
Heating and cooling
They account for almost 30 percent of a building's energy use. By transferring heat between the building and the earth using a system that circulates heat-absorbing liquid through underground wells, a building can reduce energy usage. A combined heat-and-power plant, fueled by natural gas, operates at up to 90 percent efficiency and supplies the power that the solar panels cannot. |
|










